Computer Guide
All of these components work together to create a functional computer system. Depending on the specific purpose of the computer, you may need additional components such as sound cards, network cards, or specialized hardware.
Below you can see a list of all the computer parts necessary into building your own computer.
CPU (Central Processing Unit).
The CPU, or Central Processing Unit, is the primary component of a computer that executes instructions and performs calculations. It is often referred to as the "brain" of the computer. The CPU is responsible for performing the majority of the processing that takes place in a computer, including performing arithmetic and logical operations, accessing and manipulating data, and controlling the flow of data between different parts of the computer. The CPU is made up of several components, including the control unit, the arithmetic logic unit (ALU), and the cache. The control unit is responsible for fetching instructions from memory and determining which operations to perform. The ALU is responsible for performing arithmetic and logical operations on data. The cache is a small amount of memory located on the CPU that stores frequently accessed data to speed up processing. Overall, the CPU is a critical component of any computer system, and choosing the right CPU for your needs can have a significant impact on performance and functionality.

Motherboard
The motherboard is the main circuit board of a computer system and is responsible for connecting all of the other components together. It provides the physical platform for the other components to sit on and the electrical connections that allow them to communicate with each other. The motherboard is typically rectangular in shape and is mounted inside the computer case. It contains several components, including the chipset, the BIOS, expansion slots, memory slots, and connectors for peripheral devices such as USB ports and audio jacks. The chipset is a group of chips that provide communication between the CPU, memory, and other components on the motherboard. It also controls data flow to and from external devices such as hard drives and USB devices. The BIOS (Basic Input/Output System) is a small program stored on a chip on the motherboard that initializes the computer hardware and provides basic communication between the operating system and the hardware components. Expansion slots on the motherboard allow for the addition of additional components, such as graphics cards, sound cards, or network cards. The number and type of expansion slots on a motherboard can vary, depending on the intended use of the computer system. Memory slots on the motherboard allow for the installation of RAM, which provides temporary storage for data and instructions that the CPU needs to access quickly. The number and type of memory slots on a motherboard can also vary, depending on the specific model.

RAM (Random Access Memory
RAM, or Random Access Memory, is a type of computer memory that provides temporary storage for data and instructions that the CPU needs to access quickly. RAM is an essential component of any computer system, as it directly impacts the performance of the system. RAM is made up of small, integrated circuits that are mounted on small circuit boards called memory modules. These modules are then inserted into slots on the motherboard. RAM comes in different types, speeds, and capacities, and choosing the right RAM for your computer depends on the specific needs of your system. The amount of RAM a computer has can have a significant impact on its performance. More RAM allows the computer to store more data and instructions, reducing the need to access slower storage devices such as the hard drive or solid-state drive. This can result in faster application loading times, smoother multitasking, and improved overall system performance. RAM speed, measured in MHz or GHz, determines how quickly data can be accessed from the RAM. Higher speed RAM can improve performance in applications that require large amounts of data to be loaded into memory quickly, such as video editing or gaming. RAM capacity is measured in gigabytes (GB) and determines how much data and instructions can be stored in memory at once. The amount of RAM needed depends on the specific requirements of the applications you are running. For most general use applications, 8 GB to 16 GB of RAM is sufficient. However, for more demanding applications such as video editing or gaming, 32 GB or more may be required.

Hard Drive or SSD (Solid State Drive)
HDD (Hard Disk Drive) and SSD (Solid State Drive) are two types of storage devices commonly used in computers. Both serve the same basic function of storing data and programs, but they differ in how they work and their performance characteristics. HDDs are mechanical devices that use spinning disks coated with magnetic material to store data. Data is read from and written to the disks using a read/write head that moves across the surface of the disk. HDDs have been around for many years and are still widely used today due to their relatively low cost and high storage capacity. However, they are generally slower than SSDs, especially when it comes to accessing data randomly. SSDs, on the other hand, use flash memory to store data. Flash memory is a type of non-volatile memory that retains data even when power is not supplied. SSDs have no moving parts, which makes them faster and more reliable than HDDs. They are also more expensive and typically have lower storage capacities than HDDs. One key advantage of SSDs over HDDs is their speed. SSDs are typically much faster than HDDs, especially when it comes to random access of data. This means that applications load faster and the computer overall feels more responsive when using an SSD as compared to an HDD. Another advantage of SSDs is their reliability. Because they have no moving parts, they are less prone to mechanical failure than HDDs. This makes them a good choice for portable devices such as laptops, which are more prone to being dropped or bumped. However, SSDs are generally more expensive than HDDs, especially for higher capacity models. They also have a limited lifespan due to the limited number of write cycles that flash memory can withstand. Overall, the choice between an HDD and an SSD depends on the specific needs of the user. HDDs are a good choice for users who need a lot of storage space at a lower cost, while SSDs are a good choice for users who need faster access to data and are willing to pay a higher price for it. Some users may even choose to use both an HDD and an SSD, with the OS and frequently used applications installed on the SSD for faster performance, and data and files stored on the larger HDD for cost-effective storage.

Power Supply Unit (PSU)
PSU, or Power Supply Unit, is a component in a computer that provides power to all the other components. It is responsible for converting the AC (alternating current) power from the wall outlet into DC (direct current) power that is suitable for use by the computer's components. A PSU typically consists of a metal box with a fan, a power switch, and various cables that connect to the motherboard and other components such as the CPU, graphics card, and storage devices. The wattage of a PSU determines how much power it can supply to the computer components, and the efficiency rating determines how effectively it can convert the AC power into DC power. When choosing a PSU, it is important to consider the power requirements of the components in your computer. High-end components such as powerful CPUs and graphics cards require more power, so a higher wattage PSU may be necessary. It is also important to choose a PSU that has the appropriate cables to connect to your components. The efficiency rating of a PSU is measured in a percentage and indicates how efficiently the PSU can convert the AC power into DC power. A higher efficiency rating means that the PSU wastes less power as heat and is more efficient in delivering power to the components. PSU efficiency ratings typically range from 80% to 95%.

Case
A computer case, also known as a computer chassis or tower, is the enclosure that houses all the components of a computer. It serves as a protective and organizational structure for the components, and can also have an impact on the system's performance, cooling, and overall aesthetics. Computer cases come in a variety of sizes, shapes, and materials, ranging from small mini-ITX cases to large full-tower cases. The size of the case should be chosen based on the components being used, with larger cases typically able to accommodate more components and provide better cooling. The material of the case can also impact its performance and aesthetics. Common materials include steel, aluminum, and plastic. Steel cases tend to be heavier and less expensive, but provide better sound insulation and durability. Aluminum cases are lighter and more expensive, but provide better heat dissipation and aesthetics. Plastic cases are the least expensive and lightest, but provide the least amount of durability and thermal performance. The design of the case can also impact the cooling performance of the system. Cases with more fans and larger venting areas will typically provide better cooling performance. Some cases also come with features such as liquid cooling support, removable dust filters, and cable management options to help keep the system clean and organized. The aesthetics of the case can also be an important consideration for some users. Cases come in a variety of colors and designs, with some even featuring built-in RGB lighting or tempered glass panels to showcase the internal components.

GPU (Graphics Processing Unit)
A GPU, or Graphics Processing Unit, is a specialized processor designed to handle the complex calculations required for rendering graphics and images on a computer screen. GPUs are essential components for running visually demanding applications such as video games, 3D modeling software, and video editing programs. A GPU consists of thousands of small processing cores that work together to perform calculations in parallel, making them much faster than a general-purpose CPU for certain types of tasks. GPUs also have their own dedicated memory called VRAM, which is used to store the data needed to render graphics. When choosing a GPU, it is important to consider factors such as performance, compatibility with other components, and price. Performance can be measured by looking at the GPU's clock speed, number of processing cores, and amount of VRAM. Compatibility with other components can be determined by checking the motherboard's PCIe slot type and power supply requirements. The two major GPU manufacturers are NVIDIA and AMD, each with their own lines of GPUs. NVIDIA's GPUs are typically known for their superior performance and feature set, while AMD's GPUs are known for their competitive pricing and value. In addition to gaming and graphics rendering, GPUs are also used for other types of computationally intensive tasks such as machine learning and scientific simulations. As such, GPUs have become an increasingly important component in many areas of computing beyond just gaming and graphics.

Cooling System
A computer cooling system is a critical component for maintaining the temperature of the computer components within safe operating limits. Excessive heat can cause components to malfunction or even fail, making proper cooling an essential consideration for any computer system. There are several types of cooling systems used in computers, including air cooling, liquid cooling, and passive cooling. Air cooling is the most common method used in consumer desktop computers. This method uses fans to circulate air through the case, over the components, and out through vents or exhaust ports. Air coolers consist of a heat sink, which is a metal block that absorbs heat from the component, and a fan, which blows air over the heat sink to dissipate the heat. Liquid cooling systems are another option that can provide better cooling performance than air cooling. These systems use a pump to circulate a liquid coolant through a series of tubes or pipes that are attached to the components. The liquid absorbs heat from the components and then transfers it to a radiator where it is dissipated by fans. Liquid cooling systems can be more expensive and require more maintenance than air cooling, but can provide better cooling performance. Passive cooling is a method of cooling that does not require any moving parts. It is typically used for low-power devices such as smartphones and tablets. This method relies on natural convection to dissipate heat from the components using heat sinks or thermal pads. In addition to the cooling system type, there are other factors to consider when designing a cooling system for a computer. These include the size and airflow of the case, the number and type of components, and the amount of heat generated by the components.

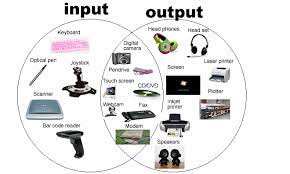
Input/output devices
Computer input and output devices are peripherals that enable users to interact with a computer system. Input devices allow users to input data and commands into the computer, while output devices display or output information from the computer. Some common input devices include:
- Keyboard: A keyboard is a standard input device that allows users to input text and commands by pressing keys.
- Mouse: A mouse is a pointing device that allows users to move a cursor or pointer on the screen and select items by clicking on them.
- Touchscreen: A touchscreen allows users to interact with the computer by touching the screen directly.
- Scanner: A scanner is a device that allows users to input documents, photos, and other physical media into the computer by scanning them.
- Microphone: A microphone is an input device that allows users to input audio into the computer by recording sound waves.
- Monitor: A monitor is a display device that outputs visual information from the computer, such as text, images, and videos.
- Printer: A printer is an output device that outputs physical copies of documents, photos, and other digital media.
- Speakers: Speakers are output devices that output audio from the computer.
- Projector: A projector is an output device that projects images and videos onto a larger screen or surface.
- Headphones: Headphones are output devices that output audio directly to the user's ears.